The main parts of an airplane include the fuselage, wings, cockpit, engine, propeller, tail assembly and landing gear. Understanding the main parts of an airplane and their functions is the first step to understanding aviation.

What are the basic parts of an airplane? From massive commercial jets to nimble, piston-powered planes, the main parts of an airplane are (relatively) the same across the board. Understanding the seven basic parts of an airplane and their functions is crucial for anyone interested in aviation or who dreams of becoming a pilot.
This article will focus on the main components of general aviation single-piston aircraft, which are commonly used for private and recreational purposes. By exploring the primary functions and key parts of an airplane, we'll help you gain a deeper understanding of how they work together to keep us soaring through the skies.
Note: For convenience, you can check out our "parts of an airplane diagram" under each section. These diagrams include the parts of an airplane labeled as a visual reference.
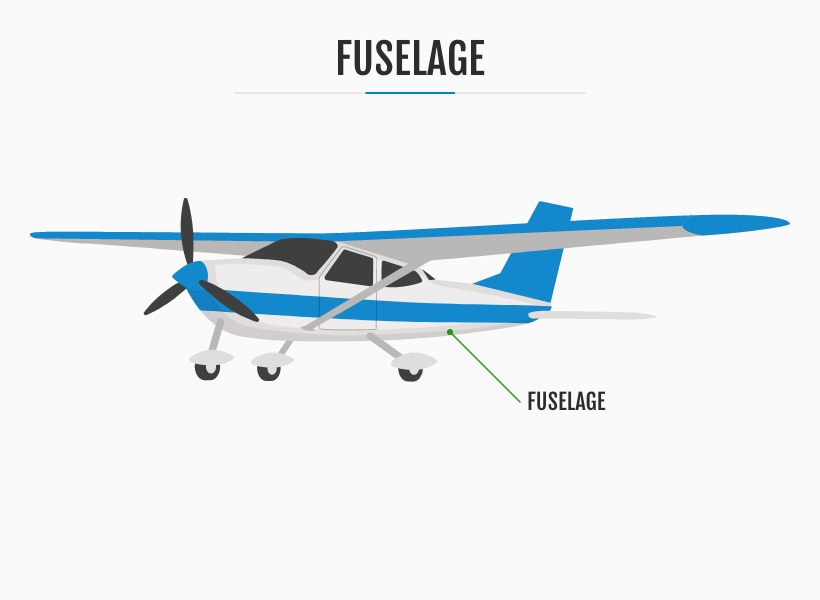
1. The Fuselage
The fuselage serves as the airplane's central and vital section, essentially the body. Beyond being a mere enclosure, these main parts of an airplane form the foundation of the aircraft's structure, providing strength, stability and integrity to support the entire flight system.
The tail number, a unique identifier for each plane, is commonly positioned towards the rear of the fuselage, close to the tail itself. This distinctive marking helps identify and track individual aircraft easily as a reference point for maintenance records, flight logs and regulatory compliance.
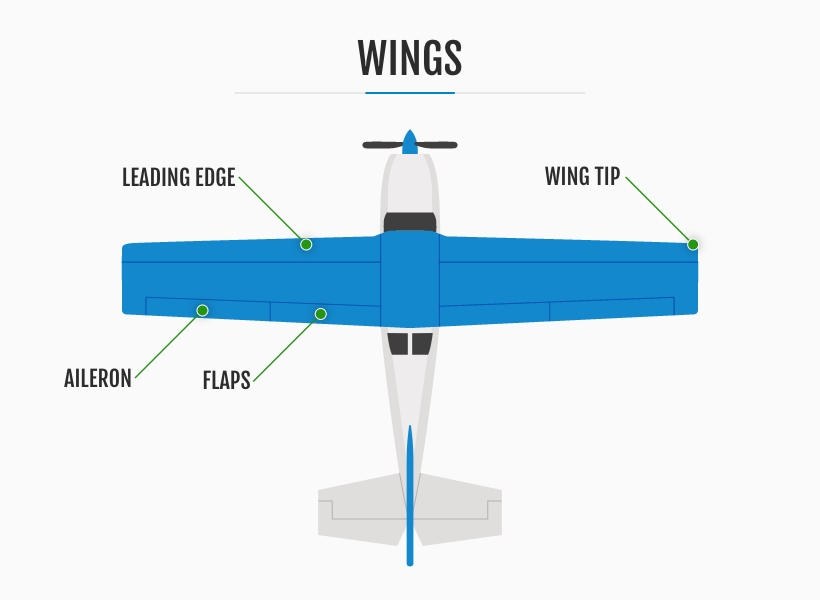
2. The Wings
The wings of an aircraft derive their name from their resemblance to the wings of a bird, serving a similar purpose. Airplanes are categorized as fixed-wing aircraft, distinguishing them from helicopters, which are considered rotary-winged. The fundamental principle behind an aircraft's ability to take flight lies in the wings' capacity to generate lift. This phenomenon occurs through a combination of the wings' aerodynamic shape and the plane's forward motion. Within the wings, we find other essential components contributing to the aircraft's overall control and performance.
What Are the Parts of an Airplane Wing?
Ailerons, a term borrowed from the French language meaning "little wing" or "fin," play a crucial role in regulating the airplane's roll or bank during flight. Working in pairs, these movable surfaces are strategically positioned on the trailing edge of the wings, allowing pilots to adjust and balance the aircraft's lateral movement with precision.
Additionally, flaps are parts of an airplane's wing that significantly reduce the stalling speed at a given weight. By modifying the shape of the wing's trailing edge, flaps enable the aircraft to maintain lift at lower speeds during takeoff and landing, ensuring safer and more controlled operations.
When examining the structure of the wings, we can also distinguish between the leading and trailing edges. The leading edge refers to the front-facing part of the wings, while the trailing edge encompasses the back edge, which includes the aileron and trim tab. This trim tab, an auxiliary control surface, assists in fine-tuning the aircraft's stability and control during flight.
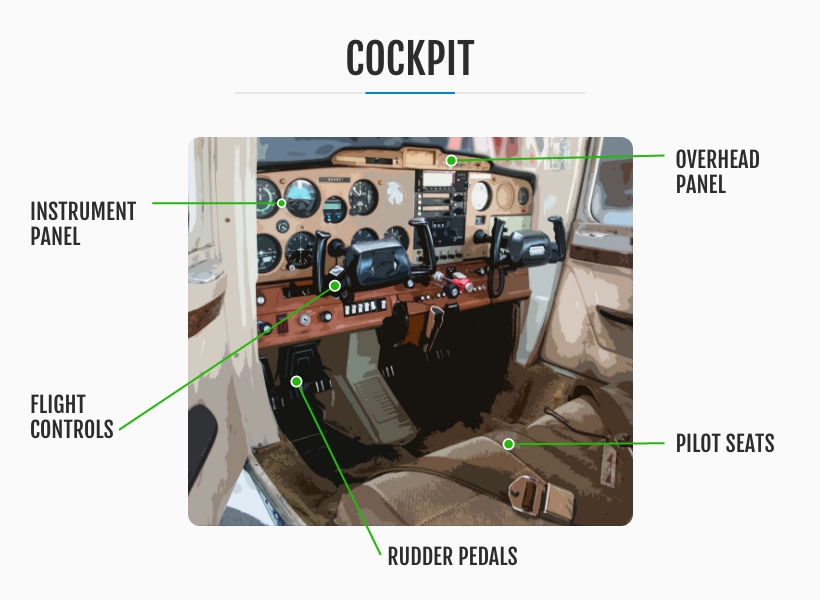
3. The Cockpit
The cockpit of an airplane serves as the nerve center where the pilot exerts control over the aircraft. It encompasses a designated area for the flight crew, housing a long list of crucial components, including flight instruments, avionics, audio/radio communications and flight controls. Within the cockpit, electronic flight instruments take center stage, with the multi-function display (MFD) acting as a versatile tool for managing vital parameters such as heading, speed, altitude and altimeter readings.
What Are the Parts of an Airplane Cockpit?
The Primary Flight Display (PFD) is one of the most integral parts of an airplane cockpit. It presents essential flight information to the pilot, including the attitude, airspeed, heading and vertical airspeed indicators. Additionally, a navigation display (ND) provides comprehensive route information, furnishing details such as waypoints, wind speed and wind direction, aiding the pilot in maintaining an accurate course.
Another crucial element within the cockpit is the flight management system (FMS), which stores and manages pertinent flight plan details, ensuring efficient navigation throughout the journey. Additionally, a transponder is strategically positioned in the cockpit, providing Air Traffic Control (ATC) with real-time information on the aircraft's location, facilitating safe and orderly air traffic management.
With the advent of modern technology, glass cockpits have become increasingly prevalent, replacing traditional analog dials and gauges. These sophisticated displays feature large LCD screens, collectively serving as electronic flight instrument displays (EFIDs).
4. The Engine
The aircraft engine is one of the most important main parts of an airplane and serves as the vital powerhouse that propels things forward. The two primary types of engines commonly utilized in aviation are piston engines and gas turbines.
Manufacturers such as Continental® Engines and Lycoming Engines have gained widespread recognition and popularity in the aviation industry. These reputable brands engineer and produce engines tailored to the specific requirements of various aircraft, encompassing both larger commercial planes and smaller private aircraft. The precision engineering and meticulous design considerations embedded in these engines contribute to their reliability, performance and compatibility with specific airframes.

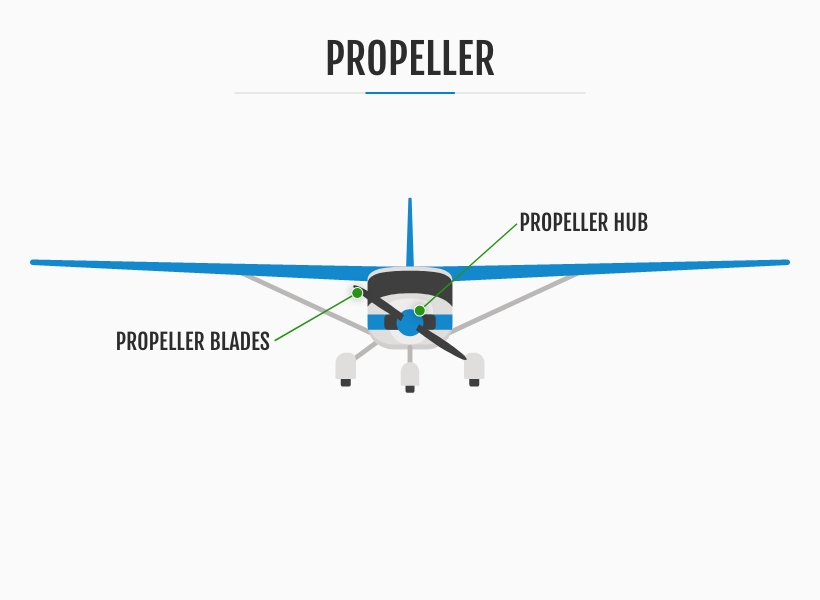
5. The Propeller
The propeller, a crucial aerodynamic device, is part of an airplane that is pivotal in converting rotational energy into propulsive force to move forward through the air. By harnessing the principles of fluid dynamics, propellers generate thrust that acts perpendicular to the plane of rotation, propelling the aircraft in the desired direction. This essential force enables the aircraft to overcome drag and propel itself through the sky.
Typically consisting of two or more blades, propellers are carefully designed and positioned around a central hub. The distribution of these blades around the hub ensures balanced and effective propulsion. The blades' precise shape, length and angle are meticulously engineered to maximize performance, optimize airflow and minimize noise. Propellers are available in different configurations to suit varying flight requirements.
6. The Tail (Empennage)
The empennage, commonly referred to as the tail or tail assembly, is a basic part of an airplane that occupies the rear section of an airplane and fulfills a crucial role in maintaining stability throughout flight. It's interesting to note the parallels between the empennage and the feathers on an arrow, as both enhance stability and control. The term "empennage" itself has French origins, derived from the French word "empenner," which translates to "to feather an arrow."
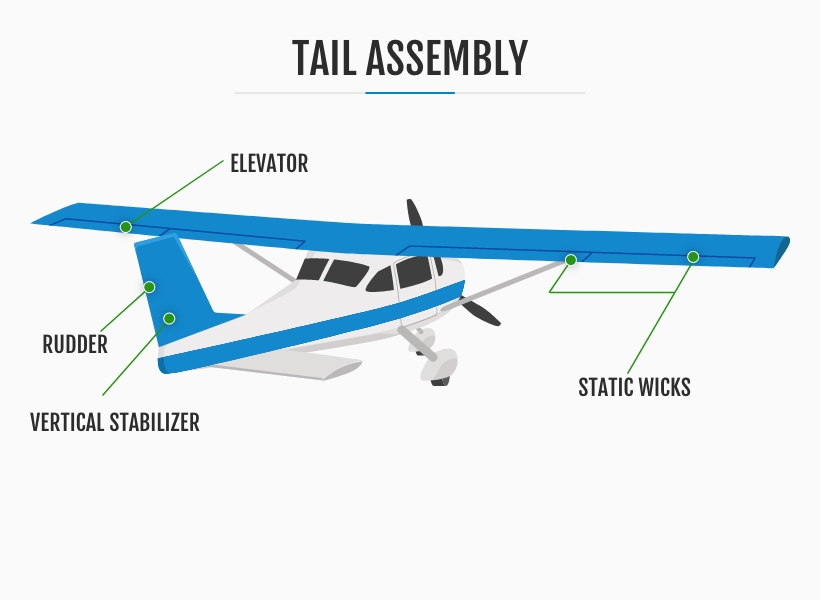
What Are the Parts of an Airplane Tail Assembly?
The parts of an airplane's tail assembly are vital to its aerodynamic performance. The vertical stabilizer, one of the key elements, stands vertically at the aircraft's rear, contributing to its stability by counteracting adverse yaw— the unwanted twisting or rotation of the aircraft's nose during flight. Connected to the vertical stabilizer is the rudder, a movable control surface that allows the pilot to exert control over the aircraft's yaw, enabling precise directional changes.
The elevator, another integral part of the airplane tail assembly, is typically found at the trailing edge of the horizontal stabilizer. The elevator controls the aircraft's pitch, allowing the pilot to adjust the aircraft's nose-up or nose-down attitude, thereby controlling the climb or descent.
The horizontal stabilizer maintains longitudinal stability by countering the aircraft's tendency to pitch up or down. It serves as a reference surface for the elevator, providing stability and control during level flight and changes in altitude.
Additionally, the tail assembly may feature static wicks, which are small, pointed devices installed on the trailing edges of the empennage. These wicks dissipate any accumulated static electricity generated by the aircraft's movement through the air, reducing the risk of electrical interference with critical communication and navigation systems.
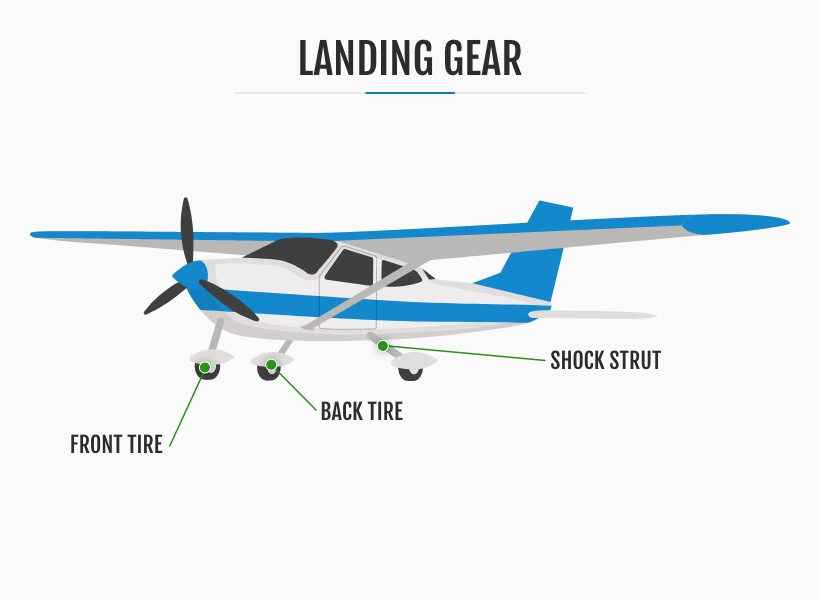
7. The Landing Gear
The landing gear is a collection of basic parts of an airplane that serve a pivotal role in facilitating takeoff and landing operations. Its primary function is to support the aircraft while on the ground, ensuring stability and preventing damage to the aircraft structure. By effectively distributing the aircraft's weight, the landing gear allows for safe taxiing, takeoff and landing procedures.
In most cases, landing gear comprises wheels, enabling smooth ground operations on conventional runways. However, certain aircraft, particularly those operating in specialized environments, are equipped with alternative landing gear configurations.
The Main Parts of an Airplane Visualized
See if you can pick out all the main parts of an airplane on the Cessna 172 Skyhawk throughout this short instructional video.
Find High-Quality Parts for Your Airplane at Air Power Inc.
At Air Power Inc., we're dedicated to providing a comprehensive range of top-quality airplane parts sourced from trusted manufacturers. What sets us apart? The convenience of having basic parts for an airplane readily available in our extensive inventory, ready to be shipped promptly to your doorstep. We prioritize having the components you need in stock and ensure that our prices are unbeatable, offering you incredible value for your investment. Explore our extensive catalog today to discover a wide array of main parts for an airplane, including renowned Continental® and Lycoming engines. Experience the ease and reliability of shopping with Air Power Inc. as you embark on your aviation journey.
Shop In-Stock Airplane Engines for Sale
Related Articles: Basic Parts of an Airplane


